The GI tract is a finely balanced environment where roughly 300 different strains of bacteria compete for space and nutrients. When there is a healthy balance (eubiosis), few symptoms exist. However, dysbiosis can occur when an over-abundance of potentially harmful organisms prevail. The natural flora balance can be upset by medications (such as antibiotics, oral contraceptives, etc.), drinking chlorinated water, or eating too many processed foods.
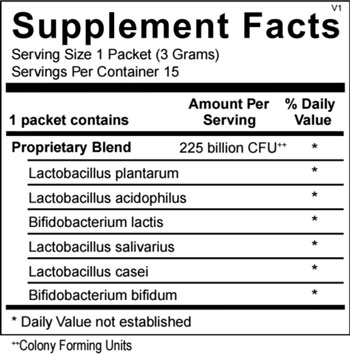
Probiotics have been extensively studied and are characterized as having broad health benefits including (1) increasing populations of healthy bacteria following microflora imbalance; (2) supporting healthy bowel function; (3) increasing the production of important short chain fatty acids that provide energy to the GI lining; (4) creating a strong immune barrier and boosting immune function; (5) aiding in the digestion of difficult to break down compounds like lactose and casein; and (6) increasing detoxification of harmful compounds.
Because probiotics are live organisms, there are many challenges associated with manufacturing and distributing probiotic supplements. For a probiotic to be effective, it must be shelf stabile through the expiration date and shown to survive passage through the harsh GI environment to the intestines for maximum benefit. The microorganisms in this product are first protected, sealed, and then freeze dried away from moisture, heat, light and oxygen. This puts the bacteria into a state of “hibernation,” allowing them to remain dormant, until they are exposed to moisture in the GI tract. This product also contains probiotic strains that have been strategically selected based on research supporting their survivability and adherence to the intestinal tract.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.