Vitamin D is a steroid vitamin, a group of fat-soluble pro- hormones that are best known for the role they play in supporting bone health and aiding in the absorption of calcium and phosphate from the gastrointestinal tract. A growing body of research highlights vitamin D’s important role in supporting other body systems, including cardiovascular and blood sugar balance, musculoskeletal strength, and neurological and immune function, enabled by vitamin D’s ability to target over 200 different genes throughout the body. At the same time, deficiency and insufficiency of this important nutrient has reached epidemic proportions around the world, making the achievement of optimal levels extremely important to overall health and wellbeing. Vitamin D3 50,000 IU is ideal for those who have difficulty achieving and maintaining peak vitamin D levels. This often includes elderly patients with low vitamin D levels, those with challenges in absorbing and maintaining vitamin D levels, and overweight patients with an elevated body mass index that impairs vitamin D circulation. For those who require an immediate boost in their vitamin D status, the vitamin D3 50,000 IU formulation is a convenient, effective way to get the substantial support they need.
Upi D 50,000
$30.00
CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
- Maintains Bone and Dental Health
- Increases Calcium Absorption and Balance
- Boosts Immune Activity
- Supports Cardiometabolic Health, Blood Sugar Balance, and Weight Loss
- Helps Increase Musculoskeletal Strength and Comfort
What is Vitamin D?
Overview
Known as the sunshine vitamin, one of the key roles of vitamin D is maintaining serum calcium and phosphorous balance. Our bodies make vitamin D by converting vitamin D2 (ergocaliferol) into D3 (cholecalciferol). Vitamin D3 is the bioidentical form of vitamin D synthesized in the skin following exposure to sunlight. Vitamin D3 is also the form which the body derives from dietary cholesterol. When calcium and phosphorus levels dip in the body, parathyroid hormone (PTH) is released to increase vitamin D conversion to the active form. D3 is then metabolized to calcitriol, a steroid hormone that helps regulate a variety of genes through the vitamin D receptor (VDR). While vitamin D is available in both the D2 and D3 forms as supplements, studies have found vitamin D3 is the preferable form. According to recent research from human clinical trials, vitamin D3 is approximately 87% more potent in raising and maintaining serum 25(OH)D concentrations, than the vitamin D2 form. [1] Vitamin D3 also produces a two- to three- fold greater storage of vitamin D than D2.[1]
Vitamin D Depletion†
While it has long been assumed that the majority of the population achieves adequate levels of vitamin D through exposure to the sun, the biosynthesis of the nutrient is affected by time of day, seasons, location, smog/pollution, clothing and sunscreen. In addition, those with darker skin require more exposure to the sun to attain adequate levels. These factors all contribute to the insufficiency seen in a growing portion of the population. It takes about 48 hours for vitamin D to be absorbed from the skin into the body and washing skin during that time period can interfere with absorption into the blood. Inadequate intake or levels of cholesterol can also inhibit the adequate production of the nutrient. Depleted levels of vitamin D may interfere with the normal development of teeth and bones, normal cell growth, and contribute to poor regulation of immune and nervous systems. Certain medications have been found to contribute to deficiency of vitamin D, including some anti-seizure medications, bile acid sequestrants, oral corticosteroids, and weight loss medications, which bind fats.[2] Bone and Dental Health† Numerous studies have highlighted the importance of vitamin D to maintaining healthy bone density. In one 2013 study, 52 overweight men and women with suboptimal vitamin D levels were given either 7,000 IU of cholecalciferol daily or a placebo for 26 weeks. The vitamin D group significantly increased vitamin D levels in the blood and improved biomarkers of bone health. [2, 3]
Cardiometabolic Health and Blood Sugar Balance†
In light of the role that vitamin D plays in a variety of tissues and body systems, it comes as no surprise that much research from recent years has underscored its contribution to cardiometabolic wellness.[5] There is accumulating evidence that calcitriol helps strengthens cardiomyocyte function, vascular smooth muscle cells, and the vascular endothelium. Low levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D are associated with diminished cardiovascular health.[6] In a recent study of 222 participants, slow coronary function was significantly higher in those with insufficient blood levels of the vitamin[7]; optimal vitamin D status has also been linked with a 40% cardiovascular system protective effect, as well as maintenance of healthy blood pressure levels.[8,9] Vitamin D has also been shown to support healthy blood sugar metabolism.[10,11]
Immune Health and Modulation†
One of the more profound functions of vitamin D is its ability to modulate immunity. An important recent study suggested that improving vitamin D status significantly affects the expression of genetic pathways linked to immune activity.[12] Vitamin D has been shown to boost the immune response by up-regulating specific genes that increase cellular production of natural compounds that protect us against pathogens. [13]
Musculoskeletal Comfort†
Numerous studies also point to the key role of vitamin D in supporting musculoskeletal strength and comfort.[14] In one study, among 62 adult patients with nonspecific musculoskeletal discomfort, over 95% had vitamin D deficiency and responded to replenishment of vitamin D. Moderate deficiency of vitamin D has also been shown to predict knee discomfort over a five-year period and hip discomfort over two years.[15]
References
- Heaney RP, et al. Vitamin D3 is more potent than vitamin D2 in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Met 2011;96(3); E447-E452.
- http://umm.edu/health/medical/altmed/supplement/ vitamin-d
- Wamberg L, Pedersen SB, Richelsen B, Rejnmark L. The effect of high-dose vitamin d supplementation on calciotropic hormones and bone mineral density in obese subjects with low levels of circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin d: results from a randomized controlled study. Calcif Tissue Int 2013 Jul;93(1):69-77.
- Cauley JA, Lacroix AZ, Wu L, Horwitz M, Danielson ME, Bauer DC, Lee JS, Jackson RD, Robbins JA, Wu C, Stanczyk FZ, LeBoff MS, Wactawski-Wende J, Sarto G, Ockene J, Cummings SR. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and risk for hip fractures. Ann Intern Med. 2008 Aug 19;149(4):242-50.
- Wang C. J Diabetes Res. Role of vitamin D in cardiometabolic diseases. J Diabetes Res 2013; 2013:243934. Epub 2013; Feb 25.
- Zittermann A, Koerfer R. Vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of coronary heart disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2008 Nov;11(6):752-7.
- Oz F, Cizgici AY, Oflaz H, Elitok A, Karaayvaz EB, Mercanoglu F, Bugra Z, Omer B, Adalet K, Oncul A. Impact of vitamin D insufficiency on the epicardial coronary flow velocity and endothelial function. Coron Artery Dis 2013 May 20.
- Ng LL, Sandhu JK, Squire IB, Davies JE, Jones DJ. Vitamin D and prognosis in acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol 2013 Feb 13.
- Martini, L.A. and Wood, R.J. Vitamin D and blood pressure connection: update on epidemiologic, clinical, and mechanistic evidence. Nutr Rev 2008; 66(5):291-297.
- Teegarden D, Donkin SS. Vitamin D: emerging new roles in insulin sensitivity. Nutr Res Rev 2009 Jun;22(1):82-92.
- Chiu KC, Chu A, Go VL, Saad MF. Hypovitaminosis D is associated with insulin resistance and beta cell dysfunction. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004 May;79(5):820-5.
- Hossein-nezhad A, Spira A, Holick MF. Influence of vitamin D status and vitamin D3 supplementation on genome wide expression of white blood cells: a randomized double-blind clinical trial. PLoS One 2013;8(3):e58725.
- Cannell JJ, Vieth R, Umhau JC, Holick MF, Grant WB, Madronich S, Garland CF, Giovannucci E. Epidemic influenza and vitamin D. Epidemiol Infect 2006 Dec;134(6):1129-40.
- Abbasi M, Hashemipour S, Hajmanuchehri F, Kazemifar AM. Is vitamin D deficiency associated with nonspecific musculoskeletal pain? Glob J Health Sci 2012 Nov 11;5(1):107-11. 15. Laslett LL, Quinn S, Burgess JR, Parameswaran V, Winzenberg TM, Jones G, Ding C. Moderate vitamin D deficiency is associated with changes in knee and hip pain in older adults: a 5-year longitudinal study. Ann Rheum Dis 2013 Apr 17.
DIRECTIONS
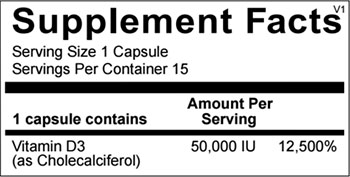
1 capsule per week. This product is a high dose vitamin D capsule that is not typically intended for long-term daily use. Please consult your health care professional if you are unsure of the appropriate dose.
DOES NOT CONTAIN
Gluten, yeast, artificial colors and flavors.
CAUTIONS
This product is a high dose vitamin D capsule that is not typically intended for long-term daily use. Please consult with your healthcare practitioner if you are unsure of the appropriate dose. If you are pregnant or nursing, consult with your physician before taking this product.
† This statement has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.